Healthcare organizations today face growing pressure to modernize their IT infrastructure, deploy digital health solutions, and maintain compliance—all while reducing costs and improving patient outcomes. In this context, healthcare IT outsourcing has become a strategic solution, not just a cost-cutting measure. From small private clinics to enterprise hospital systems and venture-backed healthtech startups, outsourcing IT services is now a widespread practice shaping the future of care delivery.
What Is Healthcare IT Outsourcing?
Healthcare IT outsourcing refers to the delegation of technology-related services to external providers with expertise in software development, infrastructure management, security, cloud computing, and digital health platforms. Instead of hiring and managing in-house technical teams, healthcare organizations contract external vendors or managed service providers (MSPs) to handle specific IT functions or entire systems.
This can include:
- Custom software development (e.g., electronic health records, telehealth apps, appointment scheduling platforms)
- Cloud and infrastructure management
- IT helpdesk and support services
- Cybersecurity and compliance consulting
- Integration with third-party systems (e.g., labs, imaging, pharmacies)
- Data analytics, AI model deployment, and automation
Outsourcing can be project-based, time-bound, or ongoing—depending on whether the goal is to build a digital product, support existing systems, or scale IT operations long-term.
Why Are Hospitals, Clinics, and Healthtech Startups Outsourcing IT?
The adoption of Healthcare IT consulting and outsourcing in healthcare is driven by a combination of economic, operational, and regulatory factors. Even the most well-funded hospitals face talent shortages and cost constraints, while startups must move quickly to validate ideas and reach patients.
1. Access to Specialized Talent
Most healthcare providers do not have in-house expertise in full-stack software development, AI, FHIR/HIPAA-compliant infrastructure, or secure app deployment. Outsourcing gives them immediate access to experienced engineers, DevOps professionals, and security experts who understand healthcare’s nuances.
2. Faster Time-to-Market
Healthtech startups and provider networks often face pressure to roll out apps and services faster. By working with a ready-made outsourcing team, they avoid delays in hiring, onboarding, and training internal staff.
3. Cost Optimization
Outsourcing reduces fixed costs associated with full-time developers, system admins, and IT leadership. Offshore and nearshore teams can provide the same output at 30–60% lower cost compared to in-house U.S. or EU-based staff.
4. Regulatory Compliance Support
HIPAA, GDPR, and HL7/FHIR standards add significant complexity to digital health systems. Outsourcing firms with healthcare-specific experience can help design systems that are compliant by design, minimizing regulatory risk.
5. Focus on Core Care Delivery
Clinicians and healthcare administrators want to spend less time on technology operations and more on improving patient care. Outsourcing shifts the IT burden to professionals, freeing up bandwidth for medical priorities.
6. Scalability and Flexibility
A hospital launching a telemedicine service or a startup releasing a remote patient monitoring app may need to scale quickly. Outsourcing allows for elastic staffing—ramping up or down as needed—without long-term commitments.
How This Guide Helps CIOs, CTOs, and Founders Evaluate Outsourcing Decisions
Whether you’re leading digital transformation for a hospital group or building a new virtual care platform, the decision to outsource healthcare IT is high-stakes. Choosing the wrong vendor, underestimating compliance risk, or overpaying for underqualified teams can derail your strategy. This guide is designed to help decision-makers across the healthcare ecosystem navigate IT outsourcing confidently and strategically.
In the pages that follow, we provide a complete overview of:
- The current healthcare IT outsourcing market and its trajectory
- Which IT services are commonly outsourced in healthcare, and why
- Benefits, risks, and hidden tradeoffs of outsourcing
- How to choose between offshore, onshore, and nearshore partners
- Cost benchmarks, pricing models, and typical project budgets
- Security, HIPAA compliance, and due diligence considerations
- Use cases, vendor selection tips, and future industry trends
If you’re asking questions like “How do I reduce my EHR upgrade cost without compromising security?”, “Is outsourcing safe for handling patient data?”, or “What are the top countries for healthcare software development?”, this guide will give you clear, evidence-backed answers.
Ultimately, the goal is not just to inform—but to empower healthcare leaders to make informed, risk-aware, and future-ready outsourcing decisions. By understanding the nuances of healthcare IT outsourcing, you can avoid common pitfalls, accelerate innovation, and unlock better outcomes for both your patients and your organization.
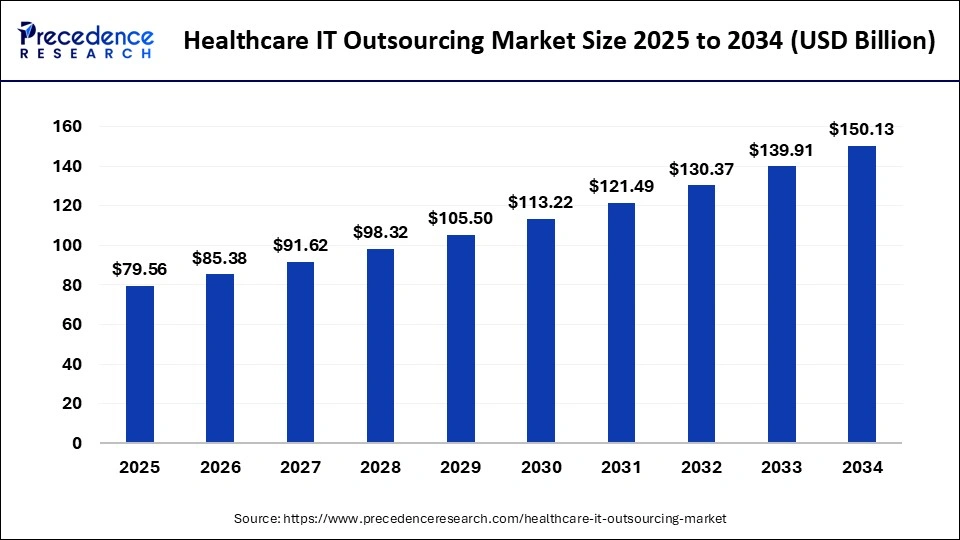
Did you know? The global healthcare IT outsourcing market size is projected to reach approximately USD 150.13 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.31% from 2025 to 2034.
Image Source: precedenceresearch
What Services Are Commonly Outsourced in Healthcare IT?
Outsourcing in healthcare IT spans a wide range of services, from building electronic health records (EHR) systems to managing cloud infrastructure and ensuring cybersecurity compliance. These services are not just peripheral functions—they are often mission-critical for care delivery, patient engagement, and operational continuity. Hospitals, clinics, and digital health companies outsource to fill talent gaps, speed up innovation, and reduce overhead while ensuring alignment with industry regulations like HIPAA and HL7.
Below is a detailed breakdown of the most commonly outsourced services, with real-world examples illustrating their value.
1. Custom Software Development
Custom software development remains one of the most outsourced components of healthcare IT. Providers and startups often require tailored solutions that align with unique workflows, clinical protocols, or regional compliance requirements.
Key areas include:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems
- Hospital Information Systems (HIS)
- Patient portals and health management apps
- ePrescription and lab management systems
Real-World Scenario:
A private hospital group in the UK needed to digitize patient records and consolidate systems across four branches. Instead of building an internal team, they outsourced to a healthtech software vendor in Eastern Europe. The outsourced partner built a modular EHR system with customizable templates for GP visits, lab integration, and patient communication tools—delivered in 8 months at half the cost of in-house development.
Outsourcing custom development provides:
- Reduced time-to-market
- Access to healthcare-focused development teams
- Modular design with future-proof architecture
2. Mobile and Web App Development
Mobile-first health applications are transforming how care is delivered and consumed. From teleconsultation apps to patient monitoring tools, these applications need continuous updates, security audits, and compliance checks—making them ideal for outsourced development teams.
Common use cases:
- Patient-facing mobile apps for scheduling, reminders, and remote monitoring
- Doctor apps for teleconsultation, record access, and case documentation
- Web portals for diagnostic labs, insurance validation, and third-party coordination
Real-World Scenario:
A U.S.-based digital therapeutics startup outsourced the development of its HIPAA-compliant software for chronic pain management to a vendor in India. The project included native iOS and Android apps, Bluetooth integration with wearable devices, and FHIR-based data sync with EHRs. The result was a scalable product that secured FDA clearance and entered commercial trials within a year.
Outsourcing mobile/web development ensures:
- Faster iterations and releases
- Seamless integration with clinical systems
- Lower costs for cross-platform builds
3. IT Infrastructure and Cloud Services
With increasing data volumes and demand for 24/7 uptime, healthcare organizations rely on external partners to manage cloud migration, server configuration, backup systems, and infrastructure security.
Services often outsourced:
- Cloud migration (to AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Infrastructure monitoring and patching
- DevOps and CI/CD pipelines
- Virtual machines and database hosting
Real-World Scenario:
A regional hospital system in Texas transitioned its legacy EHR and billing systems to Microsoft Azure with the help of an offshore managed service provider. The outsourced team set up hybrid cloud storage, Kubernetes-based deployment, and automated disaster recovery—meeting HIPAA and HITECH compliance benchmarks.
Benefits of outsourcing infrastructure:
- Always-on availability with managed SLAs
- Expertise in cloud security architecture
- Reduced capital expenses on physical servers
4. Cybersecurity and Compliance Management
Data breaches in healthcare are costly—averaging over USD 10 million per incident in the U.S., according to IBM. Given the complexity of HIPAA, GDPR, and other frameworks, cybersecurity is frequently outsourced to specialized firms.
Outsourced cybersecurity services include:
- Risk assessments and audits
- Vulnerability scanning and penetration testing
- Endpoint detection and threat response
- Data encryption and access control setup
- HIPAA compliance audits and training
Real-World Scenario:
An oncology-focused telemedicine provider experienced a minor ransomware attempt. They engaged an outsourced security partner who implemented advanced endpoint protection, audit logging, and two-factor authentication across their stack. Since then, the startup has passed multiple compliance audits and maintains SOC 2 Type II certification.
Why outsource security?
- 24/7 threat monitoring and incident response
- Domain-specific knowledge of healthcare data risks
- Reduced internal burden for compliance documentation
5. AI, Analytics, and RPA Implementations
Advanced data analysis, predictive modeling, and robotic process automation (RPA) are transforming clinical decision-making and operational efficiency. However, these systems require data scientists, ML engineers, and integration specialists that few internal IT departments can support.
Outsourced AI services may include:
- Predictive modeling for diagnosis or readmission
- NLP tools for processing clinical notes
- RPA for billing, claims, or appointment reminders
- Chatbots and AI agents for patient triage
Real-World Scenario:
A hospital network in Germany partnered with a Ukrainian AI vendor to develop a machine learning model that flags early-stage sepsis based on EHR data. The outsourced team built and validated the model on anonymized datasets and helped integrate it into the hospital’s EHR system via a RESTful API.
AI outsourcing advantages:
- Lower experimentation costs
- Access to cutting-edge tools and frameworks
- Accelerated model deployment and evaluation
6. IT Support and Managed Services
Support functions—especially after-hours or tier-1 requests—are widely outsourced to MSPs or BPOs. Healthcare organizations benefit from 24/7 ticket resolution, system monitoring, and lower staffing requirements.
Common managed services:
- Helpdesk and L1–L3 support
- System maintenance and monitoring
- Network support and incident management
- Vendor management for SaaS platforms
Real-World Scenario:
A network of primary care clinics in Canada outsourced IT support to a bilingual MSP based in Mexico. The team handles 85% of support tickets without escalation, covering EHR login issues, printer connectivity, and device failures—freeing up internal staff for higher-order tasks.
Benefits include:
- SLA-backed response times
- Round-the-clock availability
- Cost-effective multilingual support
7. Integration Services (FHIR, HL7, APIs)
Integrating disparate systems—labs, pharmacies, imaging centers, and insurance databases—is one of the most technically demanding areas of healthcare IT. Outsourced experts in HL7, FHIR, and healthcare APIs make these integrations seamless.
Services include:
- FHIR/HL7 integration with EHRs
- API development and testing
- Custom middleware for legacy systems
- Data mapping and normalization
Real-World Scenario:
A U.S.-based healthtech company launching a home diagnostics service hired an Indian integration partner to connect lab results with existing EHRs using FHIR-compliant APIs. This ensured near-real-time data sync and allowed physicians to access lab results from within their existing workflows.
Why outsource integration?
- Deep protocol expertise (HL7 v2/v3, CDA, FHIR)
- Avoid reinventing common interfaces
- Faster interoperability with fewer bugs
The healthcare industry increasingly depends on outsourced partners to deliver high-quality, compliant, and scalable IT services. From core systems like EHRs to emerging technologies like AI agents and automation bots, outsourcing enables faster innovation and better patient outcomes at a reduced cost. As complexity grows, providers must focus on choosing partners with strong domain expertise, proven delivery models, and a track record of regulatory compliance.
Whether you’re a hospital CIO evaluating cloud migration or a startup CTO launching a virtual care platform, understanding these outsourced service categories is essential for building a modern, secure, and competitive digital healthcare ecosystem.
Benefits of Outsourcing Healthcare IT
Healthcare providers today face the dual challenge of advancing digital transformation while managing resource constraints and compliance burdens. For hospitals, specialty clinics, healthtech startups, and even public health systems, outsourcing healthcare IT offers a strategic path to deliver robust technology solutions without overextending internal teams. The benefits go far beyond simple cost reduction—outsourcing unlocks operational flexibility, technical excellence, and regulatory confidence.
If you’re asking yourself “Why should a healthcare startup consider outsourcing its tech development?” or “Can hospitals maintain data security while relying on external vendors?”, this section provides a detailed look at the strategic benefits of healthcare IT outsourcing—grounded in practical examples and long-term outcomes.
1. Cost Savings and Capital Efficiency
The most immediate and measurable advantage of outsourcing is cost control. Healthcare IT outsourcing enables organizations to shift from a high fixed-cost model (hiring full-time developers, security experts, IT admins) to a more predictable operational expenditure (OpEx) model.
Key cost efficiencies include:
- Lower labor costs in offshore/nearshore regions
- No infrastructure overhead (e.g., hardware, office space, benefits)
- Reduced cost of delay (faster delivery = earlier ROI)
- Elimination of underutilized internal IT headcount
Real-World Example:
A small healthtech firm building a virtual primary care platform outsourced its full-stack development and DevOps to a team in Eastern Europe. The result: A HIPAA-compliant MVP was launched in 5 months for 60% less than the estimated U.S. build cost—enabling faster investor traction and earlier revenue.
Why this matters: For early-stage health startups or budget-constrained hospitals, outsourcing creates financial headroom to innovate without overcommitting capital.
2. Access to Specialized Expertise
Building modern healthcare systems—EHR integrations, AI-enabled diagnostics, FHIR APIs—requires deep expertise across technologies and compliance standards. Most in-house IT teams simply don’t have the experience or resources to cover every domain.
Outsourcing opens access to:
- Healthcare-specific engineers and architects
- Cybersecurity professionals with HIPAA/GDPR credentials
- Cloud specialists (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Integration experts (FHIR, HL7, DICOM, CDA)
Use Case:
A radiology center in California needed a PACS-to-cloud migration with DICOM compression and secure viewer access. They outsourced to a vendor in India that had implemented over 20 similar projects. The outsourced team completed the project in weeks—something the internal IT team couldn’t scope, much less deliver.
Bottom line: Outsourcing brings immediate access to mature technical capabilities without hiring delays, skill gaps, or learning curves.
3. Faster Time-to-Market for Digital Health Products
In healthcare, delays in launching new tools can cost lives, lose patients, or burn investor goodwill. Outsourcing accelerates time-to-market through established workflows, pre-built modules, and teams ready to execute.
How outsourcing speeds delivery:
- Dedicated sprints without internal distractions
- Agile teams with healthcare domain templates
- Concurrent development and testing processes
- Round-the-clock development cycles (due to time zone differences)
Startup Scenario:
A telepsychiatry startup in Europe outsourced mobile app development, backend infrastructure, and compliance validation. Their outsourced partner delivered a beta product within 12 weeks, enabling pilot deployment in NHS clinics and securing additional seed funding.
Takeaway: If speed is strategic—whether for clinical trials, payer contracts, or patient acquisition—outsourcing becomes a competitive advantage, not a cost center.
4. 24/7 Support and Operational Scalability
Healthcare doesn’t sleep—and neither can its IT systems. Outsourced providers offer 24/7 monitoring, global service desks, and elastic support models that adapt to your needs.
Benefits include:
- Tier 1/2/3 helpdesk coverage across time zones
- Performance monitoring and alert response
- Staffing flexibility during rollouts or incidents
- Support for multiple languages and locations
Use Case:
A hospital chain operating in both the U.S. and LATAM outsourced its IT support desk to a bilingual provider with follow-the-sun coverage. The vendor maintained >99.9% uptime across cloud systems, resolving most user incidents within 20 minutes. This would’ve required at least 10 FTEs in-house.
Scalability matters: As digital tools grow across departments and patient volume increases, outsourcing ensures consistent support without hiring cycles or internal stress.
5. Focus on Core Healthcare Delivery
Healthcare leaders—CMOs, CNIOs, and CIOs—don’t want their teams bogged down in patching servers or debugging mobile APIs. By outsourcing, organizations can refocus internal resources on clinical operations, strategy, and innovation.
What this means practically:
- IT teams manage outcomes, not inputs
- Clinical staff aren’t burdened with tech troubleshooting
- R&D and care quality teams can innovate faster
Scenario:
A hospital implementing a remote patient monitoring (RPM) solution outsourced platform setup, device provisioning, and app updates. Internal teams focused on onboarding patients and collecting outcome data instead of dealing with firmware or app crashes.
Strategic clarity: Outsourcing allows organizations to prioritize patient care, not code management.
6. Built-In Compliance Assistance (HIPAA, GDPR, HL7, FHIR)
Healthcare is one of the most heavily regulated industries globally. Building software or handling patient data means compliance with privacy laws and standards like:
- HIPAA (U.S.)
- GDPR (Europe)
- PIPEDA (Canada)
- HL7, FHIR, DICOM for interoperability
- SOC 2, ISO 27001 for cloud and vendor assurance
Trusted outsourcing firms offer:
- Pre-built security templates
- Encryption and audit logging practices
- BAA and DPA contract frameworks
- Compliance-aware DevOps workflows
Real-World Example:
A U.S. urgent care network outsourced the modernization of its scheduling and billing software to a certified HITRUST partner. The outsourcing firm managed all encryption, tokenization, and logging requirements—passing the next HIPAA audit with zero findings.
Why this matters: Compliance failure is not just a legal risk—it’s a business risk. Outsourcing to experienced vendors mitigates regulatory exposure and enhances trust with patients and partners.
The benefits of outsourcing healthcare IT are not hypothetical—they are operationally proven, financially sound, and strategically essential. Whether you’re launching a new digital health product, scaling infrastructure, or replacing a legacy system, outsourcing gives you speed, safety, and flexibility.
By tapping into global talent, reducing fixed costs, and ensuring regulatory alignment, healthcare organizations of all sizes—from startups to hospital networks—can accelerate innovation while staying focused on what matters most: delivering safe, effective, and equitable care.
Risks and Challenges of Outsourcing in Healthcare
Healthcare IT outsourcing offers undeniable advantages—cost efficiency, technical agility, and access to specialized talent. However, it also comes with significant risks, especially in an industry where data sensitivity, patient safety, and regulatory compliance are paramount. For CIOs, CTOs, and healthcare founders, it’s not enough to ask “What can outsourcing do for us?”—you must also ask “What could go wrong, and how do we prevent it?”
In this section, we address the core challenges of outsourcing healthcare IT, explore their real-world implications, and outline practical solutions to mitigate risk. If you’re wondering “Is outsourcing healthcare IT safe for patient data?”, the answer depends on your vendor selection, governance, and contractual safeguards.
1. Data Privacy and HIPAA Risks
Healthcare data is among the most regulated and sensitive categories of information globally. A single breach can lead to multi-million-dollar fines, reputational damage, and loss of patient trust.
Key risks include:
- Unauthorized access to Protected Health Information (PHI)
- Inadequate data encryption in transit or at rest
- Poor audit trails and access logging
- Non-compliant subcontractors
Real-World Incident:
In 2023, a U.S. behavioral health provider experienced a breach through an offshore IT support vendor who used shared admin credentials and stored unencrypted backups in a public cloud. Over 40,000 patient records were exposed, triggering a HIPAA fine and class-action litigation.
Solution:
- Execute a HIPAA-compliant Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with any vendor handling PHI
- Ensure end-to-end encryption, MFA, and role-based access control
- Limit PHI exposure via data minimization and anonymization
- Vet vendors with HIPAA, GDPR, or ISO 27001 certifications
Outsourcing can be secure, but it requires proactive security design, contractual compliance, and vendor accountability—not blind trust.
2. Vendor Lock-In and Knowledge Drain
When a healthcare organization outsources its core infrastructure or software development, it risks becoming dependent on the vendor’s proprietary knowledge, systems, or codebase. This vendor lock-in can make it difficult or costly to switch providers or take work back in-house.
Consequences include:
- No access to source code or infrastructure documentation
- Poor knowledge transfer when changing vendors
- Inability to maintain systems independently
- High switching costs or contract termination penalties
Use Case:
A European hospital outsourced the development of its EHR portal but failed to secure source code ownership. When the vendor abruptly shut down, the hospital had no ability to update or migrate the platform, leading to months of service disruption.
Mitigation:
- Ensure IP ownership and source code access is explicitly stated in the contract
- Mandate regular documentation and knowledge-sharing sessions
- Avoid hard dependencies on proprietary tools or custom stacks
- Plan for a transition or exit strategy upfront
Lock-in isn’t just about contracts—it’s about operational resilience. The more dependent you are, the more vulnerable your systems become.
3. Communication and Time Zone Challenges
Misaligned communication is one of the most common pain points in offshore outsourcing. Even highly competent vendors can deliver subpar results if the requirements are misunderstood, or updates are delayed due to time zone lags.
Typical problems include:
- Poorly defined requirements and vague briefs
- Lack of real-time feedback loops
- Delayed responses across continents
- Cultural gaps in communication style or hierarchy
Example:
A U.S.-based digital health startup working with a team in Southeast Asia struggled to align on API specifications. Misinterpretation caused multiple reworks, delayed the release by six weeks, and nearly lost a payer contract.
Recommendations:
- Use overlapping work hours with daily or bi-weekly standups
- Rely on structured communication tools like Jira, Confluence, Loom
- Define tasks and deliverables in precise, testable terms
- Invest in bilingual or culturally aligned project managers
Outsourcing across borders requires communication discipline and tooling rigor, not just English fluency.
4. Quality Control and Scope Creep
Without a strong governance process, outsourced healthcare projects often suffer from:
- Inconsistent coding standards
- Poor documentation
- Unstable builds or regressions
- Uncontrolled expansion of scope (“scope creep”)
In clinical settings, a software bug isn’t just an inconvenience—it could delay a diagnosis, misreport lab values, or trigger billing errors.
Common Scenarios:
- Vendors overpromise, underdeliver, then request timeline extensions
- Rapid iteration leads to incomplete testing or regressions
- Vague milestones make it impossible to assess project health
Quality Assurance Framework:
- Set quality gates for each sprint or milestone
- Enforce automated testing and code reviews
- Define and lock deliverables before project start
- Include penalties or rework clauses in the contract
Healthcare software must function flawlessly and compliantly—not “close enough.” Robust QA should be built into every outsourced engagement.
5. Solutions: Due Diligence, NDAs, SLAs, and Documentation
The risks outlined above are real, but they are also manageable. The key lies in creating a governance framework that reduces ambiguity, enforces accountability, and anticipates failure modes.
Due Diligence:
- Vet vendors based on healthcare experience, compliance track record, and references
- Review technical capability, DevOps maturity, and post-deployment support policies
Legal and Contractual Safeguards:
- NDA: Ensure confidentiality and define penalties for data leaks
- BAA: Required under HIPAA; mandates security obligations for handling PHI
- SLA: Set uptime guarantees, response times, and escalation workflows
- IP & Exit Clause: Define who owns the work and how transitions occur
Documentation:
- Require vendors to deliver up-to-date technical documentation, API specs, compliance artifacts, and deployment playbooks
- Perform quarterly audits or review cycles for long-term contracts
Outsourcing is safest when it’s governed like a partnership, not a black box.
So, is outsourcing healthcare IT safe for patient data? The honest answer is: only when it’s done with strict controls, transparent processes, and compliance-first thinking. The risks are real—but so are the tools to mitigate them. With proper vendor selection, legal safeguards, and communication discipline, outsourcing can deliver not just technical execution but strategic resilience.
Healthcare organizations that treat outsourcing as a high-trust, high-accountability endeavor—backed by contracts, audits, and checkpoints—are far more likely to succeed than those who view it as a one-time cost-saving tactic.
Onshore vs Offshore vs Nearshore Outsourcing in Healthcare IT
Choosing the right outsourcing model is one of the most strategic decisions in healthcare IT development. Whether you’re launching a patient portal, integrating FHIR-compliant APIs, or modernizing your EHR system, selecting the right geography and partner engagement model can mean the difference between success and avoidable delays. The three primary models—onshore, offshore, and nearshore—offer distinct trade-offs in terms of cost, talent access, time zones, legal compliance, and long-term scalability.
If you’re wondering “What’s the best outsourcing model for healthcare software development?”, the answer depends on your organization’s priorities: cost efficiency, communication ease, compliance risk tolerance, or proximity for collaboration. This section breaks down the differences to help you make an informed decision.
Definitions and Key Differences
- Onshore Outsourcing: Engaging a vendor in the same country as your organization (e.g., a U.S. hospital hiring a U.S.-based development agency).
- Offshore Outsourcing: Partnering with vendors in distant countries, typically with significant time zone and cost differences (e.g., India, Philippines).
- Nearshore Outsourcing: Working with vendors in neighboring or nearby countries with similar time zones (e.g., U.S. organizations outsourcing to Latin America; European firms working with Eastern Europe).
1. Cost Comparison
Offshore models typically offer the highest cost savings. For instance, full-stack healthcare developers in India or the Philippines may cost 50–70% less than equivalent talent in the U.S. or Western Europe.
- Onshore (U.S., UK, Germany): $100–$200/hour
- Nearshore (Mexico, Poland, Romania): $50–$90/hour
- Offshore (India, Philippines, Vietnam): $25–$50/hour
Cost-Sensitive Scenarios:
A U.S. healthtech startup building a remote patient monitoring (RPM) platform may opt for an offshore team in India, cutting total build costs in half while meeting HIPAA through proper compliance measures.
2. Time Zone and Communication Considerations
Time zones directly impact project velocity, feedback loops, and daily collaboration. Offshore teams may only overlap 1–2 hours per day, which can slow down decision-making unless the vendor adjusts their work hours.
- Onshore: Full overlap and real-time collaboration
- Nearshore: 4–8 hour overlap, good for agile collaboration
- Offshore: Minimal overlap; requires asynchronous communication discipline
Use Case:
A European hospital outsourcing to a Romanian firm (nearshore) experienced real-time coordination during agile sprints and faster turnaround than previous offshore engagements.
3. Talent Availability and Specialization
Offshore and nearshore hubs have cultivated deep expertise in healthcare IT over the last two decades. India, in particular, is home to major healthcare tech firms building for U.S. and UK markets, while Eastern Europe has strong credentials in cybersecurity, compliance, and custom software.
Region | Talent Strengths |
India | Full-stack dev, EHRs, AI, FHIR, HIPAA compliance |
Philippines | Support services, RCM, voice/chat, HIPAA-trained staff |
Eastern Europe (Poland, Ukraine, Romania) | Cloud infrastructure, medtech, GDPR, DevOps |
United States | Regulatory alignment, embedded teams, clinical domain knowledge |
High-Stakes Project Example:
A U.S. hospital integrating AI diagnostics into its EHR system needed both compliance and precision. They selected a dual model: offshore AI model training in India and onshore integration/testing in the U.S.
4. Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Healthcare outsourcing must comply with strict regulations like:
- HIPAA (U.S.)
- GDPR (EU)
- PIPEDA (Canada)
Onshore and nearshore partners often have an easier time aligning with these laws due to local legal familiarity and data residency. Offshore vendors must demonstrate compliance via BAAs, encryption standards, audits, and data localization strategies.
Key Legal Risks:
- Data sovereignty: Offshore partners may store data in jurisdictions not aligned with HIPAA/GDPR
- Enforcement: Pursuing legal remedies may be harder across borders
- Subcontractors: Offshore teams may further outsource to unknown third parties
Mitigation Measures:
- Sign BAAs and DPA contracts
- Require ISO 27001, SOC 2, or HITRUST certification
- Use data anonymization and role-based access control
5. Cultural Fit and Language Proficiency
Smooth communication isn’t just about time zones. Language clarity, responsiveness, and cultural understanding play vital roles in healthcare, where mistakes can have clinical or legal consequences.
- India, Philippines: High English proficiency, neutral accents, large healthcare BPO sectors
- Eastern Europe: Strong technical writing, structured communication
- Latin America (for U.S. firms): Cultural affinity, direct communication, bilingual teams
- U.S./UK: Native fluency and aligned expectations, highest cost
Example:
A bilingual support desk in the Philippines delivered 24/7 L1 support for a Canadian telehealth platform with >92% CSAT, offering empathy and clarity that exceeded previous onshore helpdesk KPIs.
Final Recommendation: What’s the Best Model for Healthcare Software Development?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. Instead, the optimal model depends on your risk tolerance, budget, timeline, and technical complexity.
- Choose Onshore if:
- You’re building mission-critical clinical systems with complex compliance
- Your team requires constant real-time collaboration
- You can afford premium rates
- You’re building mission-critical clinical systems with complex compliance
- Choose Nearshore if:
- You want agile development with cultural and timezone alignment
- Your team is based in the U.S. or Europe and needs moderate savings
- You require GDPR-aligned vendors or hybrid teams
- You want agile development with cultural and timezone alignment
- Choose Offshore if:
- You’re building a product MVP, AI models, or backend platforms at scale
- You have tight budgets but strong governance (e.g., documented specs, senior PMs)
- You’re willing to invest in documentation and security controls
- You’re building a product MVP, AI models, or backend platforms at scale
For many healthcare organizations, a hybrid approach—e.g., offshore development with onshore compliance review or nearshore DevOps—is the most balanced solution.
How to Choose the Right Healthcare IT Outsourcing Partner
Choosing the right outsourcing partner is the single most important decision in any healthcare IT project. The quality, compliance, and sustainability of your software—or even your entire care delivery platform—can depend on it. Whether you’re building an EHR system, a HIPAA-compliant telemedicine app, or integrating FHIR interfaces, partnering with the wrong vendor can lead to security failures, development delays, and expensive rework.
So, if you’re wondering “How do I find a reliable healthcare IT outsourcing company?”, the answer begins with a rigorous evaluation process rooted in technical capability, healthcare domain experience, regulatory competence, and long-term accountability.
1. Start With a Checklist of Non-Negotiables
Before comparing vendors on pricing or turnaround time, define a baseline checklist that every healthcare IT partner must meet.
Core Evaluation Criteria:
- Healthcare-Specific Technical Skills
- Proficiency in languages like Java, Python, React, Node.js
- Experience with EHR platforms (Epic, Cerner, OpenEMR), FHIR, HL7, DICOM
- Familiarity with cloud platforms (AWS HealthLake, Azure for Health)
- Proficiency in languages like Java, Python, React, Node.js
- Domain Experience
- Case studies or references from past healthcare clients
- Understanding of clinical workflows, medical billing, or patient engagement
- Comfort with terminology (PHI, CPT codes, HIE, PACS)
- Case studies or references from past healthcare clients
- Compliance Readiness
- Demonstrable knowledge of HIPAA, GDPR, PIPEDA, and HITRUST
- Ability to sign and adhere to Business Associate Agreements (BAAs)
- Clear policies on encryption, logging, data retention, and access control
- Demonstrable knowledge of HIPAA, GDPR, PIPEDA, and HITRUST
If a vendor cannot demonstrate domain fluency or compliance capabilities, they are not suitable for healthcare—even if technically strong.
2. Evaluate Their Portfolio and Past Clients
The best predictor of future performance is past success in similar healthcare environments. A strong outsourcing partner will have a verifiable portfolio of projects within healthcare or life sciences.
What to look for:
- Live healthcare products they’ve helped build or scale
- Specialty areas like telehealth, remote monitoring, EHR integration, AI diagnostics
- Client types: hospitals, insurance companies, healthtech startups, labs
- Case studies detailing architecture, compliance approach, and outcomes
Example:
If you’re developing a chronic care management app, shortlist vendors who’ve built patient-facing mobile apps with device integration and secure messaging—not just general app developers.
3. Assess Certifications and Security Practices
Security and compliance cannot be afterthoughts in healthcare. Vendors must follow industry best practices, document their processes, and ideally hold third-party certifications.
Look for:
- Certifications:
- ISO 27001 (information security management)
- SOC 2 Type II (controls and audits)
- HITRUST CSF (especially for U.S.-based cloud systems)
- ISO 27001 (information security management)
- Security Hygiene:
- Regular internal audits and penetration testing
- Secure DevOps pipelines and access control policies
- Staff training on HIPAA, data handling, and phishing prevention
- Regular internal audits and penetration testing
- Contractual Protections:
- NDA and IP clauses
- BAA (HIPAA-required)
- Clear escalation and remediation processes for incidents
- NDA and IP clauses
Always ask: How do you ensure HIPAA compliance in your software development lifecycle?
4. Dig Into Client Reviews and References
Vendor websites often highlight polished case studies—but actual client experiences provide a clearer picture of reliability, communication, and long-term support.
Research Tips:
- Clutch.co, GoodFirms, and G2 for client testimonials
- Request direct references from healthcare clients (not generic ones)
- Ask for retention data: How long do clients typically stay with them?
- Investigate any negative reviews or delays on platforms like Upwork or LinkedIn
Sample questions for references:
- How effectively did the vendor understand your healthcare use case?
- Did they meet regulatory requirements (HIPAA, GDPR, etc.)?
- How did they handle unexpected issues or scope changes?
- Were communication and documentation transparent and timely?
A truly reliable healthcare IT outsourcing firm will be open to reference checks and transparent about past challenges.
5. Ask the Right Questions During Vendor Interviews
Don’t just evaluate the proposal—assess the people, processes, and culture. Your outsourcing partner should act as an extension of your internal team.
Key questions to ask:
- “What healthcare projects have you delivered in the past 2 years?”
- “How do you handle PHI in development and QA environments?”
- “Can you show us your compliance framework (HIPAA, GDPR, ISO 27001)?”
- “Do you use subcontractors or third-party developers?”
- “How do you onboard new healthcare clients and define scope?”
- “What SLAs and uptime commitments do you offer for post-launch support?”
- “Do we retain IP ownership, and is the codebase version-controlled?”
- “Can you walk us through a recent incident or challenge you faced, and how you resolved it?”
Their answers will reveal more about maturity, transparency, and ability to handle complexity than any sales presentation.
6. Start With a Pilot Project Before Full Commitment
Even after extensive evaluation, the real test is how well the vendor delivers in practice. A pilot phase allows you to validate their:
- Communication discipline
- Compliance hygiene
- Technical accuracy
- Timeliness
- Responsiveness to feedback
Recommended pilot formats:
- A fixed-scope sprint (e.g., build login + scheduling module)
- A design and compliance audit
- A 4–6 week integration POC (e.g., FHIR API connector)
Use the pilot as both a technical and cultural trial. If the vendor fails to deliver at the pilot stage, it’s far better to walk away than proceed into full-scale development.
Finding a reliable healthcare IT outsourcing company isn’t just about choosing the lowest bidder—it’s about selecting a long-term partner who understands the unique regulatory, technical, and human challenges of building digital health systems. The ideal vendor will not only write clean code but also navigate HIPAA audits, design intuitive workflows for clinicians, and resolve bugs at 3 AM if needed.
By following a structured evaluation process—rooted in domain expertise, compliance alignment, client validation, and pilot testing—you can de-risk your outsourcing decision and build healthcare products that are scalable, secure, and patient-centered.
Cost of Healthcare IT Outsourcing
When planning to outsource healthcare IT services, cost is often one of the first considerations—and rightly so. However, cost should not be viewed in isolation. In healthcare, where compliance, security, and uptime are mission-critical, the cheapest option can quickly become the most expensive if it leads to rework, regulatory violations, or service outages.
So, how much does it cost to outsource an EHR platform, or any other major healthcare IT project? The answer depends on multiple factors—scope, region, pricing model, and technical complexity. This section offers a comprehensive breakdown of healthcare IT outsourcing costs, enabling more accurate budgeting and vendor evaluation.
1. Common Pricing Models in Healthcare IT Outsourcing
Understanding the pricing model is essential to controlling both upfront and lifecycle costs. The three most prevalent engagement models are:
1.1 Fixed Price Model
In this model, the project has a well-defined scope, and the vendor delivers it at an agreed-upon price. It’s ideal for:
- MVPs or PoCs with tightly defined deliverables
- UI/UX design and prototyping sprints
- One-time integrations (e.g., HL7, FHIR connectors)
Pros: Predictable costs, low overhead, defined timeline
Cons: Low flexibility; any change in scope leads to change requests and renegotiation
1.2 Time & Materials (T&M)
You pay for actual developer hours worked. This model is suitable for:
- Agile projects with evolving requirements
- Long-term engagements with unknown variables
- Projects with in-house product managers or CTOs
Pros: High flexibility, faster iterations
Cons: Budget overruns if not managed properly
Read: Time and Material vs. Fixed Price Contract : Comparison
1.3 Dedicated Team or Staff Augmentation
You hire a dedicated offshore or nearshore team on a monthly or hourly rate. These developers work like extensions of your internal team.
Pros: Scalability, alignment, long-term continuity
Cons: Requires strong internal management and documentation
2. Regional Cost Comparison: U.S. vs India vs Eastern Europe
Labor costs vary widely across regions, with no compromise in capability if you choose reputable vendors.
Region | Avg Hourly Rate (USD) | Notes |
United States | $120–$200 | Highest costs, strongest compliance alignment |
Western Europe | $100–$160 | High-quality delivery, GDPR native |
Eastern Europe | $40–$90 | Strong talent, moderate cost, solid English fluency |
India | $25–$60 | Most cost-effective for complex builds, deep healthcare experience |
Philippines | $20–$45 | Excellent for support, BPO, RCM, and helpdesk outsourcing |
Latin America (Nearshore for U.S.) | $35–$75 | Great time zone overlap, bilingual support |
Example:
A HIPAA-compliant telemedicine MVP built in the U.S. might cost $250,000–$400,000. The same project built by an Indian outsourcing partner may cost $90,000–$150,000, assuming similar scope and security standards.
3. Major Cost Drivers in Healthcare IT Projects
Project budgets in healthcare IT are influenced by factors beyond simple developer rates. Understanding these drivers is crucial for accurate vendor selection and planning.
3.1 Technology Stack
- React Native, Flutter, Node.js, Python, and .NET are commonly used in healthcare projects.
- Projects using cutting-edge stacks (e.g., AWS HealthLake, FHIR servers, AI/ML) typically cost more due to the need for niche expertise.
3.2 Regulatory Compliance
- Adding HIPAA/GDPR support increases testing, logging, encryption, and documentation costs.
- Building in audit trails, secure authentication, and BAAs can increase the budget by 15–30%.
3.3 Project Complexity
- An MVP with basic appointment booking is far less complex than a platform integrating with Epic, HL7, or imaging systems.
- Complex workflows (multi-role, EHR access, real-time video) significantly raise time and cost.
3.4 Support & Maintenance Requirements
- Post-launch support (L2/L3 helpdesk, security patches, cloud infra monitoring) is often charged monthly.
- A typical ongoing support retainer ranges from $2,000 to $15,000/month, depending on coverage hours and response SLAs.
4. Typical Budget Ranges by Project Type
Here’s a high-level cost estimate based on global averages and common project scopes:
Project Type | Estimated Budget (USD) |
HIPAA-Compliant Mobile App (MVP) | $80,000 – $150,000 |
EHR Customization or Module Build | $100,000 – $250,000 |
HL7/FHIR Integration | $25,000 – $70,000 |
Telehealth Platform (Video + EHR + Billing) | $150,000 – $300,000 |
Remote Patient Monitoring Platform | $100,000 – $200,000 |
AI Diagnostic Model Integration | $60,000 – $150,000 |
Healthcare Chatbot (Triage + FAQ) | $20,000 – $50,000 |
Patient Portal with Billing + Messaging | $70,000 – $120,000 |
These estimates assume outsourced development by experienced healthcare vendors in Eastern Europe or India, including QA, DevOps, documentation, and basic compliance.
When outsourcing healthcare IT, the key is not to pursue the lowest bidder—but to find the best value for the level of risk, compliance, and innovation your project demands. A vendor offering a $40/hour rate might end up costing more in the long run if their team lacks domain knowledge or HIPAA experience.
If you’re asking “How much does it cost to outsource an EHR platform?”, the honest range is $150,000 to $400,000, depending on whether you’re building a lightweight EHR from scratch, customizing an open-source base (e.g., OpenEMR), or integrating with commercial systems like Epic or Cerner. Compliance, feature scope, integration requirements, and vendor quality are what ultimately determine that number.
By aligning your outsourcing model, region, and budget with your strategic goals, you can build healthcare systems that are not just cost-effective—but secure, compliant, and clinically valuable.
Read: Healthcare App Development Cost
Compliance and Data Security Considerations
Compliance and data security are the foundation of any healthcare IT outsourcing arrangement. Unlike other industries, healthcare organizations are legally obligated to protect patient data under laws such as HIPAA, GDPR, and PIPEDA. Failure to meet these standards not only exposes patient records but also invites lawsuits, audits, and fines that can cripple your organization.
If you’re asking “How do I ensure HIPAA compliance when outsourcing healthcare IT?”, the answer lies in designing both your software systems and vendor relationships around rigorous security and regulatory protocols. This section outlines the core frameworks, tools, and contractual protections you need to confidently outsource healthcare IT while maintaining full compliance.
1. Regulatory Frameworks: What You Must Comply With
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) – U.S.
Applies to any entity handling Protected Health Information (PHI). It mandates:
- Administrative, physical, and technical safeguards
- Patient consent protocols and access logs
- Breach notification rules
- Business Associate Agreements (BAAs)
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) – EU & International Companies
Mandates data minimization, consent management, breach notification within 72 hours, and the “right to be forgotten.” Applies to any company handling personal health data of EU citizens, regardless of vendor location.
HITRUST CSF – Risk and Compliance Framework
Combines multiple standards (HIPAA, ISO, NIST, PCI) into a certifiable framework. A HITRUST-certified vendor is often considered enterprise-ready for U.S. healthcare systems.
ISO 27001 – Global Security Standard
Specifies requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an information security management system (ISMS). Not healthcare-specific, but highly valued in vendor evaluations.
Bottom line: If your vendor doesn’t understand these frameworks, they are not qualified to handle healthcare data—regardless of technical skills.
2. Ensuring Compliance in Offshore Outsourcing
Offshore outsourcing often triggers compliance concerns due to jurisdictional complexity, data sovereignty, and visibility gaps. However, compliance is possible with the right safeguards in place.
Offshore Compliance Checklist:
- Choose certified vendors (ISO 27001, HITRUST, SOC 2 Type II)
- Execute a HIPAA-compliant BAA with clearly defined PHI handling obligations
- Require local laws compatibility with HIPAA/GDPR (e.g., Indian IT Act, Philippine Data Privacy Act)
- Confirm physical security measures at offshore locations (access control, CCTV, staff training)
Data Residency and Sovereignty:
Ensure PHI is stored within the U.S. or GDPR-aligned jurisdictions unless specifically permitted. Cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP offer region-specific storage options to maintain compliance.
Remember: HIPAA is location-agnostic—it applies based on who handles the data, not where they’re located. The responsibility ultimately lies with the covered entity or healthcare provider.
3. Technical Controls: Tools That Enforce Compliance
Compliance is not achieved through policy alone—it must be enforced technically within your applications and IT infrastructure. When outsourcing, ensure these security features are embedded in the system architecture.
Critical Tools and Practices:
- Audit Logs: Immutable tracking of all user activity and data access
- Encryption: AES-256 for data at rest; TLS 1.2+ for data in transit
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Only authorized users can access specific patient data
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Prevents unauthorized system access
- Data Masking and Anonymization: Especially for development and testing environments
- Secure DevOps (DevSecOps): CI/CD pipelines with integrated security scanning
Example:
A U.S. clinic outsourced their patient portal development to a vendor in Eastern Europe. The contract mandated end-to-end AES encryption, anonymized test environments, GitHub-based access logs, and SOC 2-certified deployment infrastructure—all of which were independently audited.
These aren’t “nice-to-have” tools—they are essential for defensible compliance.
4. Contracts That Protect You: BAA, SLA, NDA
Regulatory compliance must be backed by legally binding agreements with your outsourcing partner. Without the right contracts, you’re exposed—even if the breach occurs at the vendor level.
Business Associate Agreement (BAA)
- Required by HIPAA for any third party that touches PHI
- Defines permitted uses, security obligations, and breach response timelines
- Must include subcontractor clauses if your vendor works with others
Service Level Agreement (SLA)
- Specifies uptime, response times, and security responsibilities
- Include breach notification clauses (e.g., report within 24 hours)
- Define metrics (e.g., mean time to detect, resolve, restore)
Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA)
- Protects intellectual property, source code, PHI, and proprietary workflows
- Should extend beyond the project duration
Pro tip: Ensure that SLAs and BAAs cover development, testing, support, and infrastructure management—not just deployment.
Compliance and data security are not optional in healthcare IT—they are legally mandated and reputationally essential. While offshore outsourcing may seem risky on the surface, the reality is that with the right controls, contracts, and certified partners, it can be done safely and effectively.
So, if you’re asking “How do I ensure HIPAA compliance when outsourcing healthcare IT?”, the answer is threefold:
- Choose vendors who already work in regulated healthcare environments
- Build technical safeguards into every system and interaction
- Use watertight contracts to define responsibility, accountability, and response
Outsourcing doesn’t reduce your regulatory burden—it reshapes how you manage it. With the right diligence and documentation, it can unlock innovation without compromising security or trust.
Popular Use Cases of Healthcare IT Outsourcing
Healthcare IT outsourcing is no longer limited to basic app development or helpdesk support. Today, providers and healthtech companies outsource a wide range of high-value, mission-critical projects—from telemedicine platforms and AI-powered diagnostics to EHR migrations and virtual agents. These projects are complex, compliance-heavy, and innovation-driven—yet they are being delivered successfully through specialized outsourcing partners worldwide.
If you’re wondering “What are some real examples of outsourced healthcare IT projects?”, this section outlines six widely adopted use cases where outsourcing has directly contributed to faster delivery, cost control, and better patient outcomes. Whether you’re a hospital CIO or a digital health startup founder, these examples demonstrate how outsourcing can drive both operational and clinical value.
1. Telemedicine Platform Development
The post-COVID healthcare landscape has made virtual care a standard offering, not a niche add-on. Building a HIPAA-compliant telemedicine platform—complete with video consultations, secure messaging, scheduling, and billing—requires full-stack expertise and regulatory alignment.
Why outsource:
- Rapid prototyping and MVP delivery
- Integration with EHR systems (e.g., Epic, Cerner)
- Video SDK and encryption implementation
- Compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and HITECH
Real-World Scenario:
A U.S. behavioral health startup outsourced the development of its entire teletherapy platform to a team in Eastern Europe. The outsourced partner handled video conferencing (via WebRTC), AWS deployment, and FHIR-based data syncing with the client’s in-house EHR. The platform scaled to 10,000+ active users within 6 months and passed a HIPAA audit pre-launch.
2. EHR Migration and Integration
Migrating from legacy systems or integrating third-party platforms like labs, pharmacies, and imaging centers into a unified EHR is a highly technical process. It requires deep familiarity with healthcare data standards (HL7, FHIR, CDA), security protocols, and interoperability challenges.
Why outsource:
- Expertise in data mapping, de-duplication, and normalization
- Ability to develop middleware for legacy systems
- Cost-effective large-volume data processing
Real-World Scenario:
A hospital network in the UK outsourced the migration of patient data from three legacy EHR systems into a centralized, cloud-based FHIR server. The offshore vendor created custom parsers for HL7v2 feeds and implemented data validation pipelines. The project cut administrative overhead by 30% and improved care coordination across departments.
3. Patient Engagement Mobile Apps
Healthcare organizations are increasingly deploying mobile apps that support appointment scheduling, medication tracking, push reminders, in-app messaging, and secure document sharing. These apps improve compliance, reduce no-shows, and increase satisfaction.
Why outsource:
- Native and cross-platform development expertise (iOS, Android, React Native)
- Integration with EHRs, CRMs, and calendar systems
- Fast rollout of UI/UX with multilingual support
Real-World Scenario:
An oncology clinic in Canada partnered with a Latin American development team to build a bilingual patient companion app. Features included appointment reminders, lab result viewing, and chatbot support for side effect triage. Patient satisfaction scores rose 40% post-deployment.
4. AI-Based Diagnosis Tools
AI is revolutionizing healthcare diagnostics by enabling faster, more accurate detection of diseases. Outsourcing partners with AI/ML expertise can build models, annotate datasets, and integrate decision-support tools directly into clinical workflows.
Key outsourcing services:
- Model training and validation (e.g., radiology, pathology, dermatology)
- Integration of LLMs for summarizing clinical notes
- Deployment of AI pipelines on cloud (AWS SageMaker, Azure ML)
Real-World Scenario:
A German digital health company partnered with an Indian vendor to build an AI tool that detects diabetic retinopathy from retinal images. The outsourced team built and validated the model using over 100,000 anonymized images, integrated it with the client’s EHR using FHIR, and supported CE certification documentation.
Why AI outsourcing matters: Building healthcare-grade AI requires not just model accuracy but interpretability, validation, and integration. Outsourcing accelerates this while maintaining compliance controls.
5. Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) System Modernization
Modernizing RCM systems helps healthcare providers improve claim accuracy, reduce denials, and optimize reimbursement cycles. Yet RCM systems involve multiple modules—eligibility checks, claims processing, payer integration, and analytics dashboards.
Why outsource:
- Experience with clearinghouses and payer APIs (CMS, Medicaid, private insurers)
- Automated claims validation using AI and RPA
- Integration with EHRs and billing platforms
Real-World Scenario:
A U.S. urgent care chain outsourced its RCM overhaul to a vendor in the Philippines. The team developed a web-based claims engine, integrated payer rules, and implemented RPA bots to auto-validate ICD-10 codes and scrub claims pre-submission. The result was a 22% reduction in rejected claims within 90 days.
6. Healthcare Chatbots and AI Agents
AI-powered agents and healthcare chatbots are now handling patient triage, appointment booking, medication reminders, and even post-discharge follow-ups. These AI agents for healthcare reduce staff workload and improve patient accessibility.
Common use cases for outsourced AI agents:
- WhatsApp or SMS-based virtual nurse for chronic care follow-ups
- AI front desk assistant to route appointment queries
- LLM-powered agents that summarize patient histories or guide intake
Real-World Scenario:
A primary care startup in the U.S. partnered with an offshore team to build a GPT-4-powered WhatsApp agent that triages symptoms, books appointments, and sends automated medication reminders. The agent integrates with the startup’s EHR and CRM, reducing phone-based support volume by 60%.
Why outsource AI agent development: These agents require multi-system integration, NLP expertise, and adherence to HIPAA/GDPR—making them ideal for outsourcing to specialized teams with experience in AI orchestration tools like LangChain, AutoGen, or Make.com.
Outsourcing in healthcare IT has matured from simple staff augmentation to full-scale delivery of advanced clinical and operational systems. Whether you’re modernizing back-office billing, developing AI agents for triage, or launching a digital-first care model, the right outsourcing partner can help you move faster, stay compliant, and focus internal resources on strategic goals.
If you’re evaluating healthcare IT outsourcing, these real-world use cases serve as practical validation: it’s not only feasible—it’s a proven model for innovation, scalability, and value creation in the digital health era.
Future of Healthcare IT Outsourcing
As healthcare systems worldwide evolve toward digital-first care, the future of IT outsourcing in this sector is shifting from cost-driven back-office support to innovation-led, AI-powered strategic partnerships. The next decade will see healthcare IT outsourcing expand beyond traditional development and infrastructure management into end-to-end platform orchestration, AI agent deployment, and compliance-driven automation.
So, what’s next for the healthcare IT outsourcing market? The answer lies in the convergence of cloud-native systems, generative AI copilots, and platformization—combined with new models of hybrid service delivery that offer both technical execution and clinical insight.
1. Growing Role of AI, Machine Learning, and and Healthcare Automation Software
Artificial intelligence and healthcare automation software are no longer experimental add-ons—they’re becoming core components of outsourced healthcare IT services. Vendors are now expected to not only build applications but also embed AI into:
- Clinical decision support systems
- Claims and RCM automation
- Patient risk stratification and population health models
- Real-time triage and symptom analysis
Outsourcing partners with AI/ML capabilities are increasingly handling:
- Model development and fine-tuning (e.g., disease prediction models)
- Generative AI copilots that assist doctors during consultations
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) bots for tasks like insurance verification
What’s changing: Healthcare organizations are seeking vendors who go beyond coding—they need partners that understand how to embed intelligence within workflows.
2. Rise of AI Agents and Generative AI Copilots
Perhaps the most transformative trend is the rise of AI agents—autonomous or semi-autonomous tools that can monitor, retrieve, and act within clinical and administrative environments. These aren’t just basic chatbots; they’re context-aware assistants that integrate across systems.
Examples of outsourced AI agents in healthcare:
- WhatsApp-based appointment agents that access scheduling APIs, confirm insurance, and send reminders
- GPT-4 copilots embedded in EHRs that summarize visit notes, flag anomalies, or draft discharge summaries
- Triage agents that process intake forms and route patients to appropriate providers based on NLP analysis
Outsourcing teams are now leveraging orchestration frameworks like LangChain, AutoGen, and LangGraph to design agent workflows that align with HIPAA and GDPR, making them deployable across SMS, web, and voice interfaces.
What this means: Future outsourcing will focus on building, training, deploying, and governing AI agents—not just applications.
3. Cloud-Native Healthcare Architectures
Cloud computing has become the default foundation for scalable healthcare systems. What’s changing is how vendors are expected to architect solutions:
- Using serverless models to minimize operational overhead
- Leveraging cloud-native healthcare tools like AWS HealthLake, Azure API for FHIR, or Google Healthcare API
- Designing for elastic workloads in AI inference, imaging storage, and EHR queries
Cloud-native design is now a required skillset for top outsourcing firms, especially those serving multi-tenant SaaS health platforms and telehealth providers.
Why it matters: Outsourcing firms must now deliver compliant, cloud-optimized solutions that support AI, APIs, and global scale—without bloated infrastructure costs.
4. Shift to Platform-Based Service Delivery
As hospitals and healthtech companies increasingly adopt multiple point solutions, the future lies in platformization—where vendors offer integrated, composable stacks instead of custom apps.
Outsourcing providers are now:
- Offering white-label healthcare platforms (e.g., modular telehealth suites, FHIR integration hubs)
- Building microservice-based systems that plug into existing IT ecosystems
- Supporting ongoing DevOps, MLOps, and SecOps as managed services
Trend impact: Instead of treating software projects as “deliverables,” healthcare outsourcing is evolving into long-term, platform-centric partnerships where agility and modularity matter more than raw developer hours.
5. Emergence of Hybrid Vendor Ecosystems
Large health systems and digital health startups alike are beginning to adopt hybrid outsourcing models, where multiple vendors contribute to different parts of a project—some onshore, some nearshore, others offshore.
New models include:
- Onshore compliance leadership + offshore development
- Nearshore DevOps paired with offshore AI training
- Split teams across time zones for 24/7 continuous delivery
This vendor decentralization is driving the need for stronger coordination, interoperability standards (FHIR, HL7), and shared accountability frameworks.
Implication: The future of healthcare outsourcing will be collaborative, composable, and multi-vendor by design—requiring new management playbooks for vendor governance.
The future of healthcare IT outsourcing is no longer about transactional development—it’s about orchestrating innovation at the intersection of AI, compliance, and cloud infrastructure. Vendors will be judged not just by code quality, but by their ability to deliver intelligent systems, scale globally, and comply locally.
If you’re planning to outsource healthcare IT in the coming years, look for partners who:
- Build and deploy AI agents across secure channels
- Understand cloud-native architectures and FHIR integration
- Offer platform modularity and long-term operational support
- Are certified in security, privacy, and DevSecOps frameworks
As outsourcing shifts from execution to enablement, healthcare organizations that embrace this next-gen model will be best positioned to lead in digital transformation.
Why Aalpha for Healthcare IT Outsourcing
Aalpha is a trusted healthcare software development company and technology partner for healthcare organizations seeking to build secure, compliant, and scalable digital health solutions. With over 15+ years of experience delivering complex healthcare software across global markets—including the U.S., UK, Europe, and the Middle East—Aalpha combines deep domain expertise with agile execution and regulatory excellence.
1. Proven Healthcare IT Expertise
From medical software development such as EHR systems and FHIR integration to telehealth platforms, patient portals, and AI-based diagnostics, Aalpha has successfully delivered dozens of healthcare projects for hospitals, clinics, healthtech startups, and medical device companies. Our team understands the nuances of clinical workflows, interoperability standards, and compliance-driven architectures.
2. Full HIPAA, GDPR, and HL7/FHIR Compliance
At Aalpha, compliance is not an afterthought—it’s embedded into every line of code and every deployment. We sign HIPAA-compliant Business Associate Agreements (BAAs), conduct regular security audits, and design systems that adhere to HL7, FHIR, GDPR, and ISO 27001 standards. Whether you’re handling Protected Health Information (PHI) or operating across multiple jurisdictions, our solutions are built to be audit-ready.
3. End-to-End Development and Support
We offer full-cycle healthcare software development—including UX/UI design, architecture, development, QA, DevOps, and post-launch support. Whether you’re launching a new product, modernizing legacy systems, or scaling infrastructure, Aalpha delivers enterprise-grade reliability with startup agility.
4. AI Agent and Automation Specialists
Aalpha is at the forefront of AI agent implementation in healthcare. We design and deploy WhatsApp-based AI agents, LLM-powered clinical copilots, and RPA bots for operational efficiency. Our AI-powered solutions automate patient communication, intake, triage, and post-visit follow-ups—reducing manual load while improving patient experience.
5. Global Delivery Model with Transparent Engagement
With delivery centers in India and client offices across North America, Europe, and the Middle East, Aalpha offers flexible engagement models including fixed-price, dedicated teams, and hybrid outsourcing. Our transparent workflows, milestone-based reporting, and agile practices ensure predictable results and minimal risk.
6. Trusted by Startups and Enterprises Alike
Whether you’re a funded digital health startup building an MVP or an enterprise hospital group modernizing systems across locations, Aalpha scales to meet your needs. Our clients choose us for our healthcare focus, long-term partnership approach, and proven track record of success.
If you’re looking for a healthcare IT outsourcing partner who combines deep regulatory knowledge, technical excellence, and real-world delivery capability—Aalpha is the right choice. Let’s build something that saves time, improves care, and transforms your digital health roadmap.
Conclusion:
Outsourcing healthcare IT is no longer just an operational decision—it is a strategic move that can determine the pace, quality, and sustainability of your digital transformation. Whether you’re a hospital system looking to modernize infrastructure, a healthtech startup launching a virtual care platform, or a clinic expanding telehealth services, outsourcing enables you to tap into global expertise, accelerate innovation, and reduce costs without compromising on security or compliance.
Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the full landscape: from real-world use cases like EHR integration, AI diagnostics, and patient engagement apps, to practical considerations such as HIPAA compliance, vendor selection, and regional cost models. The evidence is clear: with the right partner, outsourcing can deliver enterprise-grade outcomes while maintaining regulatory alignment and operational control.
However, successful outsourcing requires more than selecting a vendor with technical capabilities. It demands due diligence, watertight contracts, shared accountability, and a deep understanding of healthcare-specific challenges. The best outsourcing partners are not just service providers—they are long-term collaborators who understand clinical priorities, support patient-centered design, and integrate seamlessly with your internal teams.
For early-stage startups, outsourcing offers the speed and agility to compete with larger players. For established providers, it offers the scalability and compliance coverage needed to expand services, integrate systems, and future-proof your tech stack.
So, should you outsource your healthcare IT? If your goals include faster time-to-market, better operational efficiency, scalable innovation, and full compliance—the answer is yes, but only if you do it right.
The key is selecting partners who specialize in healthcare, offer transparency and governance, and bring more than just code to the table. With the right strategy, outsourcing becomes not a risk—but a competitive edge.
FAQs on Healthcare IT Outsourcing
1. What is healthcare IT outsourcing?
Healthcare IT outsourcing is the practice of delegating technology-related services—such as software development, infrastructure management, data security, or support—to external vendors. These partners may operate onshore, nearshore, or offshore, and can provide solutions like EHR customization, mobile app development, telemedicine platforms, cloud migration, or AI implementation. Outsourcing enables healthcare providers and startups to access specialized expertise, reduce operational costs, and accelerate digital transformation while maintaining regulatory compliance.
2. How do I maintain HIPAA compliance while outsourcing?
To maintain HIPAA compliance, healthcare organizations must:
- Sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with any vendor handling Protected Health Information (PHI)
- Ensure vendors implement safeguards like end-to-end encryption, audit logging, access control, and multi-factor authentication
- Confirm that development and QA environments use anonymized or masked data
- Vet vendors for HIPAA experience, certifications (e.g., HITRUST, SOC 2, ISO 27001), and data handling protocols
Outsourcing does not reduce your compliance obligations—it shifts some operational responsibilities to the vendor under strict legal and technical controls.
3. Can I outsource to India or Eastern Europe safely?
Yes, outsourcing to India or Eastern Europe is not only safe but widely practiced by leading healthcare systems, healthtech startups, and medical device companies. However, safety and compliance depend on:
- Working with healthcare-specialized vendors
- Reviewing data residency laws and ensuring jurisdictional compatibility with HIPAA or GDPR
- Verifying that vendors follow international security standards and can operate under signed BAAs
India offers deep expertise in healthcare IT, FHIR integration, and AI development, while Eastern Europe excels in cloud infrastructure, cybersecurity, and medtech platforms. Many vendors in these regions serve clients in the U.S., UK, and EU regularly.
5. What are the disadvantages of outsourcing EHR development?
While outsourcing EHR development can be cost-effective, several risks must be managed:
- Vendor lock-in if the codebase or system architecture isn’t fully documented
- Scope creep and delayed timelines if requirements are not clearly defined
- Compliance risk if the vendor lacks HIPAA/FHIR experience
- Integration complexity if your EHR must sync with other internal or third-party systems
To mitigate these risks:
- Define clear ownership and documentation clauses
- Choose vendors with experience in healthcare data standards
- Perform compliance audits during and after development
- Start with a pilot phase before scaling
6. How do I vet a healthcare IT outsourcing partner?
Use a structured vetting process that evaluates:
- Domain expertise: Look for vendors with proven projects in EHR, telehealth, billing, or AI
- Compliance readiness: Confirm they understand HIPAA, GDPR, ISO 27001, and can sign BAAs
- Technical proficiency: Assess their experience with your desired tech stack (e.g., React, AWS, FHIR, HL7)
- Security practices: Review DevSecOps workflows, audit logging, encryption, and MFA standards
- Client references: Speak to healthcare clients they’ve worked with in the last 1–2 years
Ask questions like: “How do you manage PHI?”, “Can we access the full codebase?”, and “What’s your remediation process in case of a security incident?”
7. What’s the average project timeline for outsourced healthcare IT?
Project timelines vary based on complexity, compliance scope, and delivery model. Typical estimates:
- MVP Telemedicine App: 3–5 months
- EHR Customization: 4–8 months
- FHIR Integration or HL7 Middleware: 6–12 weeks
- RCM Automation Tool: 3–6 months
- AI Diagnostic Model Integration: 4–6 months
Always add time buffers for security audits, compliance testing, and clinical validation. Pilot projects or phased rollouts are advisable to reduce risk.
8. Is outsourcing suitable for healthcare startups?
Absolutely. In fact, many digital health startups rely on outsourcing to:
- Rapidly build and launch MVPs
- Access HIPAA-compliant infrastructure without in-house teams
- Reduce burn rate and extend runway
- Validate market fit before scaling development
Startup founders should choose outsourcing vendors with strong UX capabilities, healthcare API experience, and a track record of launching apps in the App Store, Google Play, or via web portals. Outsourcing allows startups to focus on go-to-market and compliance strategy, while experienced vendors handle execution.
9. What are common mistakes to avoid in healthcare IT outsourcing?
Some pitfalls include:
- Choosing a generalist IT vendor with no healthcare experience
- Ignoring compliance at the MVP stage (“we’ll add HIPAA later”)
- Skipping BAAs and NDAs
- Failing to document code ownership and handover processes
- Over-customizing EHRs without considering upgrade paths
Avoid these mistakes by prioritizing domain expertise, legal protections, and documentation from day one.
Healthcare IT outsourcing, when done strategically, enables faster innovation, scalable development, and full compliance. From EHR migrations to AI agent deployment, outsourcing partners can deliver secure, patient-centered systems—provided they’re vetted properly and managed with clear contracts.
Whether you’re a hospital IT leader or startup founder, the success of your outsourcing engagement will depend on how well you balance cost, speed, compliance, and trust—not just who charges the lowest rate.
Ready to bring your healthcare IT vision to life? Partner with Aalpha for secure, scalable, and compliant digital health solutions—built right, from day one.